Convenience meets expertise. Here's why Medicspot is your perfect healthcare partner.
Arthritis symptoms in hands
Many forms of arthritis can cause symptoms in your wrists, the joints of your fingers, and the base of your thumbs. These include:
The cause of many types of arthritis is unknown. Researchers are looking into the role of genetics (heredity) and lifestyle in the development of arthritis.
There are several things that may raise your risk for arthritis, including:
Sex. Most types of arthritis are more common among women, except for gout.
Genes. Certain types of arthritis run in families. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and ankylosing spondylitis, for example, are linked to certain genes.
Symptoms may include headaches, shortness of breath, chest pain, and nosebleeds. It may feel asymptomatic or present with subtle signs at first, but advanced cases include persistent headaches, difficulty breathing, chest discomfort, or nosebleeds.
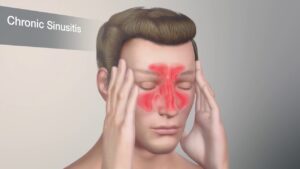
Chronic allergies are a widespread condition that affects millions of people worldwide. An allergy occurs when the immune system overreacts to a foreign substance that is typically harmless to most people. Some of the most common chronic allergies include hay fever (allergic rhinitis), eczema, drug allergies, and food allergies.
The symptoms of chronic allergies are often persistent and can be difficult to manage. Some people may experience severe or mild allergy symptoms, including:
. Sinus Congestion – Blockage or stuffiness of the nasal passages.
. Coughing – Allergic coughing is a reaction to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander.
Persistent Sneezing – A reflex action that occurs when the nasal passages are irritated by allergens.
. Itching – A common symptom of allergies that can affect the skin, eyes, nose, and throat.
. Facial Congestion – Feeling of pressure, fullness, or tightness in the face, usually around the sinuses or nasal passages.
Urticaria – Also known as hives, this is a skin condition characterized by the sudden appearance of itchy, red, or white welts or bumps on the skin.
Chronic allergies can also lead to life-threatening symptoms, such as asthma attacks and anaphylaxis.
The treatment for chronic allergies and allergy medications depends on the severity of symptoms and your medical history. Some commonly prescribed medications for chronic and seasonal allergies include:
. Singulair – A leukotriene receptor antagonist that helps to reduce inflammation and swelling in the airways, making it easier to breathe.
. Azelastine – An antihistamine that helps to reduce the symptoms of allergies, such as sneezing, itching, and runny nose.
. Prednisone pack – A corticosteroid that is prescribed for severe allergy symptoms, such as difficulty breathing or swelling of the face and throat.
. Cetirizine – An antihistamine that can be used to relieve allergy symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, and itchy or watery eyes.
. Flonase – A corticosteroid nasal spray that helps to reduce inflammation in the nasal passages.
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to diagnose your allergies and determine the best way to treat your allergies, as some medications may have negative interactions with others or have potential side effects due to undetected drug allergies.
Signs and Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease
Symptoms of Crohn’s vary widely depending on the person and on the part of the GI tract that the disease attacks.
How Crohn's Disease Affects Your GI Tract
Crohn's can affect your digestive tract in patches. Some areas may be damaged while others are completely healthy.
Fistulas and Crohn’s Disease: What to Know
Fistulas are tunnels that form between two organs or an organ and the surface of your body, due to Crohn’s inflammation.
Bowel Obstruction and Crohn's Disease
Blockage in your intestines is a common problem with Crohn’s disease.

What Causes Crohn’s Disease?
Although there are many theories about what causes Crohn's disease, none of them have been proven.
Who Gets Crohn’s Disease?
Scientists haven’t identified all causes of Crohn’s, but they’ve found certain groups of people who are at higher risk.
Gut Bacteria and Crohn’s Disease
When the gut microbiome balance is disrupted, it can make you more prone to disease, including Crohn’s disease.
How Does Smoking Affect Crohn's Disease?
Smoking doesn't cause Crohn's. But smoking can increase your risk of Crohn's, or make it more severe and harder to treat.
Diagnosing Crohn's Disease
There isn't a single test that can diagnose Crohn's. To diagnose, your doctor will gather information from many sources.
X-Ray Exams of the Digestive Tract
Your doctor can choose an abdominal X-ray to help them diagnose and keep track of your Crohn’s disease.
Your Crohn's Care Team
You’ll probably see several types of health professionals for your Crohn's. They'll work together to help you manage symptoms.
Ways to Tell if You Have the Right Crohn's Doctor
Crohn's is a lifelong illness, so you'll want someone you can count on for the long haul.
Medications for Crohn’s Disease
If you have Crohn’s disease, the right medications may keep your condition under control.
Step-Up or Top-Down for Crohn’s Disease: Treatment Options
The medications used in the step-up and top-down methods are the same. You’ll just get them in a different order.
Antibiotics and Crohn’s Disease: Help or Hurt?
Medical experts speculate that an overgrowth of bacteria is one of the causes of Crohn’s disease.
Work With Your Doctor to Manage Your Crohn's Disease
When you're managing your Crohn's disease, a great relationship with your health care team is key.
What Is Dementia?
There are many different types of dementia. Your loved one's treatments will depend on the type they have.
Early Dementia
Many older people fear that they have Alzheimer's disease because they can't find their eyeglasses or remember someone's name.
The Basics of Alzheimer's
Alzheimer's is a disease that robs people of their memory. At first, people have a hard time remembering recent events.
Alzheimer’s: Answers to Questions
An Alzheimer's diagnosis can be overwhelming. Get answers to common questions that you may have for the doctor.
Alzheimer's Disease: How It’s Diagnosed
If you think you or a loved one might be showing symptoms of Alzheimer's, it’s important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis.
Understanding Alzheimer's Disease Symptoms
There are three main phases of Alzheimer's: mild, moderate, and severe. Each stage has its own set of symptoms.
Is It Alzheimer’s or Normal Aging?
Small memory lapses happen. They're a normal part of aging -- just like creaky knees, wrinkled skin, or blurry vision.
10 Early Signs of Alzheimer’s
If memory problems are seriously affecting your daily life, they could be early signs of Alzheimer's disease.
Causes of Alzheimer's Disease
Researchers don't know exactly what causes Alzheimer's disease. There are probably a lot of things that are behind it.
Is Alzheimer’s Genetic?
No one knows the exact cause of Alzheimer's disease, but scientists do know that genes are involved.
Alzheimer's Disease in Older Men vs. Older Women
Both men and women are at increasing risk for Alzheimer’s disease as they age. But women get it more often.
Down Syndrome and Alzheimer's Disease Risk
Down syndrome increases the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. People with Down syndrome also experience premature aging.
Treatments for Alzheimer's Disease
Right now, there is no cure for Alzheimer's disease. But there are medicines that can ease some of the symptoms in some people.
How Race and Culture Can Affect Alzheimer's Care
Cultural beliefs about mental health conditions like Alzheimer’s can affect how and when one gets help.
Which Medicines Treat Dementia?
When someone you care about has dementia, their memory loss is affecting their daily life. There are medicines that can help.
Anti-Amyloid Therapies for Alzheimer’s Disease
The newest treatment approved to fight Alzheimer’s disease is a kind of drug called an anti-amyloid.
Gout symptoms involve sudden and severe joint pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness, commonly affecting the big toe. It may feel intensely painful, with joints becoming hot and sensitive.
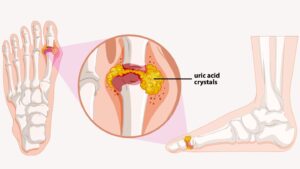
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis that causes pain and swelling in your joints, usually as flares that last for a week or two, and then resolve. Gout flares often begin in your big toe or a lower limb. Gout happens when high levels of urate build up in your body over a long period of time, which can then form needle-shaped crystals in and around the joint. This leads to inflammation and arthritis of the joint. When the body makes too much urate, or removes too little, urate levels build up in the body. However, many people with high levels of serum urate will not develop gout.
Gout causes and symptoms are primarily the result of an excess of uric acid in the bloodstream, a condition known as hyperuricemia. This excessive uric acid can lead to the formation of urate crystals, which can accumulate in the joints, typically in the big toe but also in other joints. Also decided by lifestyle factors and habits, what causes gout can also include:
. A diet rich in meat and seafood
. Drinking alcohol, especially beer
. Drinking sweetened drinks
. Obesity
. Certain medications such as thiazide diuretics and aspirin
Genetics
Gout symptoms are generally sudden and severe in the affected joint, often in the big toe, though it can occur in other joints. Common gout symptoms can include:
. Intense and sudden joint pain
. Swelling and inflammation
. Limited mobility from the affected joint
Blood pumping through the circulatory system is under pressure, much like the water in the pipes of a house. And just as too much water pressure can damage pipes and faucets, elevated blood pressure can spell trouble. Hypertension occurs when the force exerted against artery walls is abnormally high.
Over time, elevated pressure can cause a wide range of problems. Small bulges, called aneurysms, may form in blood vessels. The heart can become enlarged, increasing the danger of heart attack and heart failure. Damage to blood vessels in the kidneys can cause them to fail. Because tiny blood vessels in the eyes are especially vulnerable to damage, hypertension can lead to vision problems and even blindness.
High blood pressure -- in men and women -- is a big problem. One in every three adult Americans -- about 65 million people -- have high blood pressure, also known as hypertension. Many more are at risk of developing it. Over half of all Americans age 60 and older have it and over a lifetime, the risk of developing high blood pressure is 90%.
Typically, blood pressure increases with age. Risk of high blood pressure begins to climb when people hit age 45, although it can occur in younger people. Blacks tend to develop it younger and have more severe hypertension. Obesity or a family history of high blood pressure also increases risk.
High blood pressure is especially dangerous because people can have it for years without knowing. In fact, 1 in 3 Americans with the condition doesn’t know it.
Despite these gloomy statistics, high blood pressure is not inevitable. There is plenty you can do to prevent, delay, and treat the condition.
Blood pressure is the measure of the force of blood pushing against blood vessel walls. The heart pumps blood into blood vessels, which carry the blood throughout the body.
High blood pressure, also called hypertension, means your heart is working harder to pump blood out to the body. It's a dangerous condition and contributes to hardening of the arteries, or atherosclerosis, stroke, kidney disease, and heart failure.
High blood pressure, or hypertension, affects nearly half of adults in the U.S. Because it usually doesn’t make you feel sick, many people are surprised to hear that they have it.
However, high blood pressure can have a big impact on your health, so it is important to understand what it is, what causes it, and how you can lower it.
High blood pressure (hypertension) is often called the “silent killer” because it typically has no symptoms. However, if left uncontrolled, it can lead to serious health problems such as heart disease (heart attack), stroke, and kidney disease over time.
Although symptoms can be difficult to detect and identify, Some symptoms can include:
. Headaches - Particularly in the morning, which may be accompanied by blurred vision, dizziness, or nausea.
. Shortness of breath - Feeling breathless during physical activity or even at rest.
. Chest pain - Discomfort or tightness in the chest.
. Fatigue - Feeling tired or weak regardless of your physical or mental strain that day.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism include:
sweating
irregular heartbeat
weight loss
protruding eyes
nervousness
Symptoms of hypothyroidism include:
tiredness
weight gain
depression
abnormal bone development
stunted growth
An infant with hypothyroidism may be inactive and quiet, have a poor appetite, and sleep for long periods.
Early signs of thyroid disease include changes in your:
tolerance for hot or cold temps
menstrual cycle
energy level or mood
weight
If you or your child have one or more of these symptoms, contact a doctor.
Weight gain in hypothyroidism isn't uncommon, but it's usually only 5 to 10 pounds. Large weight gain is rare and associated with severe hypothyroidism. If your only symptom is weight gain, you probably have something other than a thyroid problem.

Thyroid disease can be tricky to diagnose. That's because its symptoms can look like those of other conditions.
For example, thyroid disease symptoms could be similar to those you might have during pregnancy. These tests help your doctor know if you have a thyroid issue:
Blood tests. One of the surest ways to diagnose a thyroid problem, these tests measure the amount of thyroid hormones in your blood. They're done by taking blood from a vein in your arm.
Imaging tests. Looking at your thyroid might answer a lot of questions. Your doctor might do an imaging test called a thyroid scan. This lets them check the thyroid for an increased size, shape, or presence of growths (nodules).
They also might do an ultrasound. This transmits high-frequency sound waves, which you can't hear, through your body. Echoes are recorded and transformed into video or photographic images. It takes 20-30 minutes.
Physical exams. Done in your doctor's office, this is a simple and painless test where your doctor feels your neck for any growths or enlargement of the thyroid.
Iodine uptake tests. If you have hypothyroidism, your doctor might do this test to find what's causing it. This tracks the amount of iodine absorbed by your thyroid gland. You get iodine from the foods you eat. It's a key ingredient of thyroid hormone, so the amount of iodine your thyroid absorbs is a good way to tell how much hormone your gland is making.
our doctor can use different ways to restore your thyroid hormone levels to normal. Each treatment depends on the type and cause of your thyroid condition.
Subacute thyroiditis treatment
Although subacute thyroiditis can bring on temporary hyperthyroidism, this condition doesn't require medical treatment.
First, the doctor asks detailed questions like:
Did the reaction come on quickly, within an hour of eating the food?
Did anyone else get sick?
How much did you eat before the reaction started?
How was the food prepared?
Did you eat anything else at the same time?
Did you take an antihistamine or do something else? Did it help?
Does this always happen when you eat that food?

If your doctor thinks a specific food allergy is likely, you may get tests to measure your allergic response.
One of these is a scratch puncture test. The doctor or technician puts a drop of a solution made with the food on your forearm or back. Then they'll prick your skin with a needle through the drop and watch for swelling or redness.
Skin tests are quick, simple, and relatively safe. But experts don't recommend making a diagnosis based on a skin test alone. Your skin test may show an allergy to a food without you having allergic reactions when eating that food. So your doctor will diagnose a food allergy only when you have a positive skin test and a history of reactions to the same food.
If you're extremely allergic and have severe reactions, skin testing could be dangerous. It also can't be done if you have severe eczema. Instead, your doctor can use blood tests such as RAST and ELISA that measure the amount of food-specific IgE. These tests may cost more, and results take longer. Again, a positive result doesn't necessarily mean you have a food allergy.
The main way to deal with food allergies is to avoid them. For highly allergic people, even tiny amounts of an allergen (as little as 1/44,000 of a peanut kernel) can trigger a reaction. Less-sensitive people may be able to have small amounts of a food that they're allergic to.
Once you've identified the food, you have to stop eating it. That may mean reading long, detailed ingredient lists because many allergy-triggering foods are in things you wouldn't expect to find them in. Peanuts, for example, may be included for protein, and eggs are in some salad dressings. At restaurants, you might have to ask about the ingredients that are in specific dishes or in the kitchen.
Even people who are very careful can make a mistake, so if you have severe food allergies, you must be prepared to treat an accidental exposure. If you've had anaphylactic reactions to a food, you should wear a medical alert bracelet or necklace. And you should carry two auto-injectors of epinephrine (Auvi-Q, EpiPen, Symjepi) and be ready to use them if you think a reaction is starting. Mild symptoms such as tingling in your mouth and throat or an upset stomach might not be an allergic reaction, but you should still give yourself an injection. It won't hurt, and it could save your life. Then call 911 or get a ride to the emergency room.
There are many ways you can ease menopause symptoms and maintain your health. These tips include ways to cope with mood swings, fears, and depression:
Eat healthfully, and exercise regularly.
Engage in a creative outlet or hobby that fosters a sense of achievement.
Find a self-calming skill to practice such as yoga, meditation, or slow, deep breathing.
Keep your bedroom cool to prevent night sweats and disturbed sleep.
Seek emotional support from friends, family members, or a professional counselor when needed.
Stay connected with your family and community, and nurture your friendships.
Take medicines, vitamins, and minerals as prescribed by your doctor.
Take steps, such as wearing loose clothing, to stay cool during hot flashes.

There are a variety of ways to treat depression, including medications such as antidepressants, brain stimulation techniques like ECT or TMS, and individual psychotherapy.
Family therapy may help if family stress adds to your depression. Your mental health care provider or primary care doctor will determine the best course of treatment for you. If you are unsure who to call for help with depression, consider checking out these resources:
Community mental health centers
Employee assistance programs
Family doctors
Family service/social agencies
Health maintenance organizations
Hospital psychiatry departments and outpatient clinics
Local medical and/or psychiatric societies
Mental health specialists such as psychiatrists, psychologists, social workers, or mental health counselors
Private clinics and facilities
State hospital outpatient clinics
University or medical school-affiliated programs
What Is Depression?
Depression is a mood disorder with a group of symptoms including constant sadness or lack of interest in life.
Depression and Sadness: When to See the Doctor
Is your sadness just a low mood that will pass in time, or is it depression?
Questions and Answers About Depression
10 answers to common questions about depression.
Depression: The Latest Research
The latest research on major depression aims to help you feel better faster, and with fewer side effects.

What Are the Symptoms of Depression?
There are a lot of signs of depression, but you may not have them all. How intense they are, and how long they last, varies.
Severe Depression Warning Signs
Severe depression has intense symptoms that may include significant appetite and weight loss, sleep problems, and more.
Spotting Depression Disguises
Depression can be sneaky, disguised in symptoms that can be hard to identify.
Depression: Recognizing the Physical Signs
We know the emotional symptoms of depression. But many with depression live with chronic pain or other physical symptoms, too.
Depression Treatment: Your Options
Your treatment plan for depression will depend on what type you have and how severe it is.
Treatment Tips
Depression can make you feel helpless. Taking charge of your treatment is one way to feel in control again. Here are some tips.
Talk Therapy
Psychotherapy is another tool in your toolkit to manage depression. And it works for lots of people.
Psychodynamic Therapy
Psychodynamic therapy helps patients explore the full range of their emotions, including feelings they may not be aware of.
As with other chronic diseases, a person with IBD will generally go through periods in which the disease flares up and causes symptoms, followed by periods in which symptoms decrease or disappear and good health returns. Symptoms range from mild to severe and generally depend upon what part of the intestinal tract is involved. They include:
Abdominal cramps and pain
Diarrhea that may be bloody
Severe urgency to have a bowel movement
Fever
Weight loss
Loss of appetite
Iron deficiency anemia due to blood loss
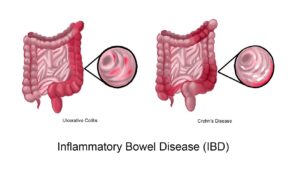
Treatment for IBD involves a combination of self-care and medical treatment.
Although no specific diet has been shown to prevent or treat IBD, dietary changes may be helpful in managing your symptoms. It's important to talk with your doctor about ways to modify your diet while making sure you get the nutrients you need. For instance, depending on your symptoms, the doctor may suggest that you reduce the amount of fiber or dairy products that you consume. Also, small, frequent meals may be better tolerated. In general, there is no need to avoid certain foods unless they cause or worsen your symptoms.
One dietary intervention your doctor may recommend is a low-residue diet, a very restricted diet that reduces the amount of fiber and other undigested material that pass through your colon. Doing so can help relieve symptoms of diarrhea and abdominal pain. If you do go on a low-residue diet, be sure you understand how long you should stay on the diet because a low-residue diet doesn't provide all the nutrients you need. Your doctor may recommend that you take vitamin supplements.
What Is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)?
IBS is a mix of belly discomfort or pain and trouble with bowel habits.
Hormones and IBS: Is There a Link?
Women are about twice as likely to have IBS as men. Growing research shows that sex hormones may be the reason.
What's the Difference Between IBS and IBD?
It’s easy to mix up these conditions, but inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) aren’t the same.
What Are the Symptoms of IBS?
We all have trouble going to the bathroom sometimes. But for those with IBS, the chronic pain and discomfort can be disabling.
The 3 Types of IBS
There are three types of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), each with different symptoms. Understand the difference between them.
IBS With Diarrhea
IBS that causes increased diarrhea is often called IBS-D.
Treating IBS With Diarrhea
People with IBS-D often find relief through dietary changes, meds, stress relief, or behavioral or alternative therapies.
Treating IBS With Constipation
The goal of treatment for IBS-C is to soothe the stomachaches, pain, and bloating that are also common symptoms.
Alternative Treatments for IBS
Some patients turn to alternative treatments such as acupuncture, dietary supplements, and herbs for help with IBS.
IBS vs. Lactose Intolerance
IBS and lactose intolerance cause symptoms that are nearly identical. But there are differences in causes and treatment.
Adding {{itemName}} to cart
Added {{itemName}} to cart